RCEP
 STOTA
STOTA  2020-11-25
2020-11-25
R C E P
This year been really tough for us: tiles manufacturer, dealers, builders and buyers. Because the Corona virus, many business and shops closed, people lose jobs, shipping line cutting, freight and other cost increased rapidly. In this situation, we must be more strong and survive from this.
Nearly at the end of this year, we hear the good news finally: Without the United States, the world's largest free trade zone--RCEP was born!

The conclusion of RCEP will greatly improve China's external trade environment, effectively promote closer trade and investment and industrial division between China and RCEP members, and provide new impetus for China's economic growth.

On 15th November 2020, the signing ceremony of the regional comprehensive economic partnership agreement (RCEP) was held by video, and the ministers of economy and trade of 15 member countries formally signed the agreement. The signing of the agreement marks the successful start of the construction of East Asia free trade area with the largest population, the most diverse membership structure and the largest development potential in the world.

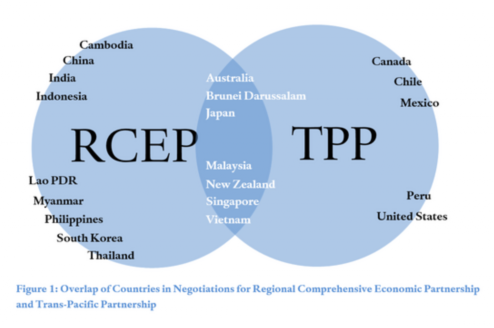
It is reported that RCEP was initiated by 10 ASEAN countries and invited six dialogue partners, including China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand and India, to participate. The purpose of RCEP is to establish a free trade agreement of 16 countries with a unified market by reducing tariff and non-tariff barriers. On November 4, 2019, India temporarily did not join the agreement because "there are important issues that have not yet been resolved".
According to the statistics of 2018, the 15 RCEP member countries will cover about 2.3 billion people, accounting for 30% of the global population; the total GDP will exceed 25 trillion US dollars, and the regions included will become the largest free trade area in the world.
So, what are the framework and trade principles of RCEP and what are the specific contents? Why does India delay joining RCEP? After RCEP comes into effect, can China realize the strategic hedging of the comprehensive and progressive trans Pacific Partnership Agreement (cptpp) and substantially reduce the losses caused by trade transfer?

On trade in goods, the RCEP has made trade liberalization and facilitation a top priority and is committed to building a high-quality free trade area that will gradually eliminate all tariff and non-tariff barriers to trade in goods. In addition to traditional tariff concessions, the RCEP has focused on rules of origin and trade facilitation.
In practice, the lack of flexibility of the single rule of origin is also one of the reasons for the low utilization rate of FTA. The RCEP draw lessons from the successful experience of the upgrade of the china-asean FTA negotiations, of rules of origin in the RCEP negotiations with "alternative" rules of origin, namely the RCEP member can choose any area value composition standard or items change rules of origin, the enterprise greatly increased use of rules of origin of the flexibility and convenience, and, more importantly, simple rules of origin to help member at a lower cost to producer interests protection area, further through regional production network.
In terms of trade in services, the RCEP will, to varying degrees, surpass THE WTO standards in different sectors and open up different subsectors with rules including market access, national treatment and most-favourid-nation treatment. RCEP members also pledged to enhance the transparency and predictability of their domestic policies, reduce the losses caused by policy changes for other member companies, and improve the business environment in the whole region.

Over the years, China has been an active participant and promoter of the RCEP. In the new round of restructuring of the global trading system, the RCEP is an important cornerstone for China to build a high-quality global free trade network. The conclusion of the RCEP will also help China and Asia win the strategic initiative in the fierce competition of global trade rule-making.
(1) Reconstructing regional value chain to provide new driving force for China's economic growth

RCEP's participation in GVCS increased from 38.3% in 2007 to 40.5% in 2017. In 2017, THE VALUE chain based exports of THE RCEP reached us $1.6 trillion, value chain based exports among regional members reached US $780 billion, and the value chain utilization rate within the region reached 48.7%.
Through the mutual opening of market access, including trade in goods and services, RCEP can reduce the dependence of China and Asian countries on the U.S. market to a certain extent, and will play an important supporting role in China's export and foreign investment.
Currently, RCEP member economies are important destinations for China's import and export trade and foreign investment. In terms of trade, in 2018, China's total trade volume with RCEP members exceeded US $1.3 trillion, accounting for 28.3% of the total import and export trade of the whole year.
- RCEP can effectively deal with the negative impact from cptpp
As another giant free trade agreement in the Asia Pacific region that will come into effect in 2019, the cptpp includes not only Canada, Mexico, Chile and Peru, but also Asian economies such as Singapore, Brunei, Malaysia and Vietnam. Due to the high standard trade rules adopted by cptpp and the high entry threshold, the non joined economies in the region, including China, suffer from the negative impact of exclusive trade transfer caused by cptpp.
Take cptpp's "rules of origin" as an example, cptpp follows the TPP's "spinning frontier" rules of origin, requiring that textiles from raw materials to processing and manufacturing are carried out in the economies of cptpp members, otherwise they can not enjoy the cptpp tariff preference. Therefore, under the restriction of cptpp's rules of origin, China's textile and clothing exports (the largest import source of furniture and toy products, textiles and raw materials, shoes, shoes and umbrellas and other light industrial products imported by Canada and other cptpp countries is China), which is not only strongly impacted by Vietnam, a member economy of CPPP, but also limited to the so-called "spinning frontier" of cptpp According to the rules of origin, China's export of textile raw materials or intermediate products to Vietnam and other cptpp economies is also hindered. Some Chinese enterprises even have to transfer to other countries and set up factories in Vietnam or other cptpp economies.
According to the model forecast of Peterson Institute of international economics of the United States, CPP will reduce China's GDP by 0.04%, welfare level by 10 billion US dollars, and export of goods by 0.2% and 9 billion US dollars. If the cptpp is expanded to include Indonesia, the Philippines, South Korea and Taiwan as members, China's GDP will drop by 0.2%, the total social welfare level will be reduced by 53 billion US dollars; the export volume of goods trade will be reduced by 0.9%, and the negative impact on China will be doubled. However, if RCEP takes effect, China can realize the strategic hedging of cptpp, greatly reduce the losses caused by trade transfer, and even obtain more obvious economic benefits in the electronic and other industries. Moreover, the larger the scope of RCEP members, the more significant the overall benefits.
- Safeguard the multilateral trade system and actively participate in the new round of reconstruction of the global trade system
In particular, the United States is increasingly dissatisfied with the existing multilateral trading system and seeks the reconstruction of a new order by destroying the order. The U.S. trade policy is putting the world trade organization overhead and building a network of free trade agreements mainly based on bilateral agreements according to its interests, thus making the multilateral trade system face a major turning point for decades. In the aspect of international trade, the so-called "reciprocal trade law" is replaced by "the most favoured country" in international trade, and the "most favored country" is replaced by "the most favored country" in international trade. This trend has shaken the multilateral trading system based on the world trade organization. The uncertainty of global economic and trade policies has risen sharply and the economic and trade system has become increasingly fragmented.
The United States has been pressing its major trading partners, including its allies, to use trade sanctions and high tariffs as a means to coerce other countries to negotiate with them according to their wishes. Although according to Article 24 (5) of the general agreement on Tariffs and trade (GATT), regional integration is allowed to exist as an exception to the most favored nation treatment and non discrimination principle of the World Trade Organization (WTO), excessive deviation from MFN principle will inevitably lead to the threat of bilateralism replacing multilateralism.
At present, the US South Korea Free Trade Agreement and the North American Free Trade Agreement have been revised, and the US Japan trade agreement has been initially formed. If the US UK free trade agreement and the US Europe free trade agreement are successfully completed in the future, the total economic volume and trade volume of this closed free trade area network with the United States as the axle will account for half of the world, and strong trade will be generated Transfer effect, and then hit the global multilateral trading system. In this way, not only the special and differential treatment of developing members under the original WTO framework will be seriously eroded, but the international trade activities of any other member will also be subject to the highly uncertain international trade governance system.

Against this background, the timely completion of the RCEP negotiations has released an important signal to the outside world that Asian economies are firmly committed to building an open world economy and supporting the multilateral trading system. Among the members of RCEP, there are both the most developed countries and the least developed countries. The economic development level of each member is very different, and the social and political systems, history and culture are not the same. So different and diverse countries can come together and reach a high-level free trade agreement acceptable to all parties. This highly inclusive North-South economic cooperation is obviously pushing forward than that of the United States The so-called "reciprocity and reciprocity" fair trade has more practical value and is of great significance to the formulation of global economic and trade rules in the future.Wish all of us could be better and better.














